JIGSAW
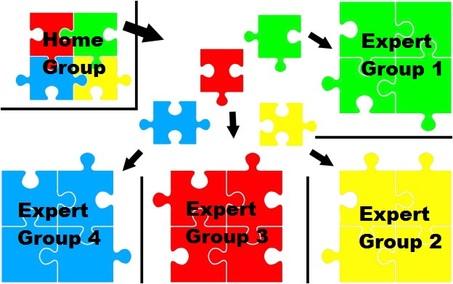
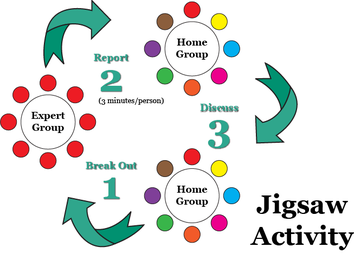
Definition/Description: Jigsaw is a cooperative learning strategy that enables each student to become an expert on a certain topic, through communication and discussion with others reading the same text, researching the same topic or unit, and then share their findings to their original “home” group. One student from each group has his/her own topic and then they meet with other students from other groups who have the same topic and they work together to decide the most important parts to share back with their original or home group to help them develop the same understanding.
Definition/Description: Jigsaw is a cooperative learning strategy that enables each student to become an expert on a certain topic, through communication and discussion with others reading the same text, researching the same topic or unit, and then share their findings to their original “home” group. One student from each group has his/her own topic and then they meet with other students from other groups who have the same topic and they work together to decide the most important parts to share back with their original or home group to help them develop the same understanding.
Differentiated instruction
- "Give students experience with small group learning skills before participating in the jigsaw strategy.
- Have students fill out a graphic organizer in the "home group" to gather all the information presented by each "expert."
- "Home groups" can present results to the entire class, or they may participate in some assessment activity.
- Circulate to ensure that groups are on task and managing their work well; ask groups to stop and think about how they are checking for everyone's understanding and ensuring that everyone's voice is heard; and
- Monitor the comprehension of the group members by asking questions and rephrasing information until it is clear that all group members understand the points" (Reading Rockets, 2015).
|
Purpose:
To give students the opportunity to be the teacher, build confidence and responsibility, and work collaboratively with other to come up with the main ideas of a text. Tips:
Content Area Examples:
Reading:
|
Specific Content Area Examples:
|
Additional Links for: Information, Lessons, and Material
References:
Aronson, E. (2015). Jigsaw Classroom: overview of the technique. Retrieved from http://www.jigsaw.org/overview.htm
Clarke, J. (2013). Pieces of the puzzle: The jigsaw method. In S. Sharan (Ed.), Handbook of cooperative learning methods. Westport CT: Greenwood Press.
Goalbook Toolkit (2015). Jigsaw Activity. [imagie]. Retrieve September 18. From https://goalbookapp.com/toolkit/strategy/jigsaw
Graphic Organizer for Jigsaw Activity/Groupwork (2011).[imagine]. Retrieved from .http://adventureswithlanguage.com/2011/03/09/graphic-organizer-jigsaw/
Jigsaw (2012). [Web Video]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtm5_w6JthA
Jigsaw (2015). Goalbook Toolkit. Retrieve from https://goalbookapp.com/toolkit/strategy/jigsaw
Jigsaws: A Strategy for Understanding Texts. (2012). [Web Video]. Retrieved on September 18. From https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/jigsaw-method
ReadingRockets. (2015). Jigsaw. Retrieved from http://www.readingrockets.org/strategies/jigsaw
Aronson, E. (2015). Jigsaw Classroom: overview of the technique. Retrieved from http://www.jigsaw.org/overview.htm
Clarke, J. (2013). Pieces of the puzzle: The jigsaw method. In S. Sharan (Ed.), Handbook of cooperative learning methods. Westport CT: Greenwood Press.
Goalbook Toolkit (2015). Jigsaw Activity. [imagie]. Retrieve September 18. From https://goalbookapp.com/toolkit/strategy/jigsaw
Graphic Organizer for Jigsaw Activity/Groupwork (2011).[imagine]. Retrieved from .http://adventureswithlanguage.com/2011/03/09/graphic-organizer-jigsaw/
Jigsaw (2012). [Web Video]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtm5_w6JthA
Jigsaw (2015). Goalbook Toolkit. Retrieve from https://goalbookapp.com/toolkit/strategy/jigsaw
Jigsaws: A Strategy for Understanding Texts. (2012). [Web Video]. Retrieved on September 18. From https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/jigsaw-method
ReadingRockets. (2015). Jigsaw. Retrieved from http://www.readingrockets.org/strategies/jigsaw